
Parity information is spread across all physical devices in the vdev. These vdevs can be configured with single, double, or triple parity (and even more in recent versions of ZFS). If there are 4 disks in a mirror vdev, the capacity that you can use to store data is the capacity of the smallest disk in that structure.

Here’s an example of a pool: zpool status The block devices can be backed by partitions or whole disks/drives. text files).Ī ZFS pool is made up of one or more groups of virtual devices or vdevs. Compression also improves read and write speeds - sometimes considerably if the information is very compressible (e.g. Compression and deduplication can be turned on to save disk space.Clones can be created from snapshots and can be promoted to take over.You can take snapshots of your filesystems and rollback to them in case of need.
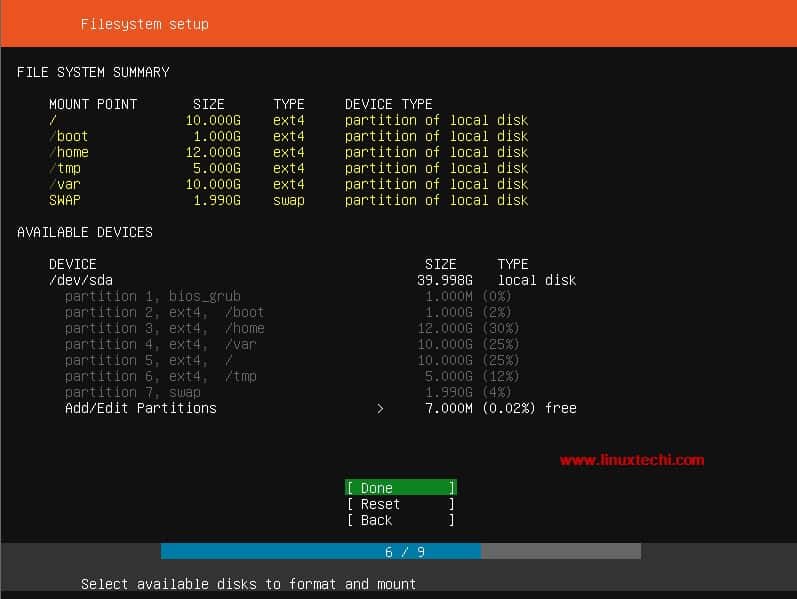
Devices can be grouped in RAID-Z arrays, similar to RAID 5, but more than three parity disks are supported.Most of the operations can be done online.This makes it possible to dynamically increase the pool size without worrying about partitioning and expanding the filesystem. A volume manager allows you to combine your physical storage devices into pools.Corrupted data will be reported and even automatically fixed if the storage pool has been setup with redundancy. Instead of “trusting” the storage device, itĬhecksums the data then stores it in separate blocks from the data itself. ZFS offers protection against silent data corruption. Since no errors have been reported by the filesystem, the backups contain the corrupted files so there is no way to recover. The drive will write incorrect data but report a successful operation. Silent data corruption can be caused by a controller fault, firmware bug, or microscopic flaw in the design of magnetic/flash memory. What is Silent Data Corruption? How Does ZFS Work?


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
